ok Prussia [a] was a historically prominent German state that originated in 1525 with a duchy centered on the region of Prussia on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It was de facto dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and de jure by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia, with its capital first in Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, in Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany.
In 1871, owing to the efforts of Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck, most German principalities were united into the German Empire under Prussian leadership, although this was considered to be a “Lesser Germany” because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during the German Revolution of 1918–19. The Kingdom of Prussia was thus abolished in favour of a republic—the Free State of Prussia, a state of Germany from 1918 until 1933. From 1932, Prussia lost its independence as a result of the Prussian coup, which was taken further in the next few years when the Nazi regime successfully established its Gleichschaltung laws in pursuit of a unitary state. The remaining legal status finally ended in 1947.[3]
The name Prussia derives from the Old Prussians; in the 13th century, the Teutonic Knights—an organized Catholic medieval military order of German crusaders—conquered the lands inhabited by them. In 1308, the Teutonic Knights conquered the region of Pomerelia with Danzig (modern-day Gdańsk). Their monastic state was mostly Germanised through immigration from central and western Germany, and, in the south, it was Polonised by settlers from Masovia. The imposed Second Peace of Thorn (1466) split Prussia into the western Royal Prussia, becoming a province of Poland, and the eastern part, from 1525 called the Duchy of Prussia, a feudal fief of the Crown of Poland up to 1657. The union of Brandenburg and the Duchy of Prussia in 1618 led to the proclamation of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701.
Prussia entered the ranks of the great powers shortly after becoming a kingdom.[4][5] It became increasingly large and powerful in the 18th and 19th centuries. It had a major voice in European affairs under the reign of Frederick the Great (1740–1786). At the Congress of Vienna (1814–15), which redrew the map of Europe following Napoleon’s defeat, Prussia acquired rich new territories, including the coal-rich Ruhr. The country then grew rapidly in influence economically and politically, and became the core of the North German Confederation in 1867, and then of the German Empire in 1871. The Kingdom of Prussia was now so large and so dominant in the new Germany that Junkers and other Prussian élites identified more and more as Germans and less as Prussians.
The Kingdom ended in 1918 along with other German monarchies that were terminated by the German Revolution. In the Weimar Republic, the Free State of Prussia lost nearly all of its legal and political importance following the 1932 coup led by Franz von Papen. Subsequently, it was effectively dismantled into Nazi German Gaue in 1935. Nevertheless, some Prussian ministries were kept and Hermann Göring remained in his role as Minister President of Prussia until the end of World War II. Former eastern territories of Germany that made up a significant part of Prussia lost the majority of their German population after 1945 as the Polish People’s Republic and the Soviet Union both absorbed these territories and had most of its German inhabitants expelled by 1950. Prussia, deemed a bearer of militarism and reaction by the Allies, was officially abolished by an Allied declaration in 1947. The international status of the former eastern territories of the Kingdom of Prussia was disputed until the Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany in 1990, but its return to Germany remains a topic among far right politicians, the Federation of Expellees and various political revisionists.
The term Prussian has often been used, especially outside Germany, to emphasise professionalism, aggressiveness, militarism and conservatism of the Junker class of landed aristocrats in the East who dominated first Prussia and then the German Empire.
Contents
Symbols[edit]


History of Brandenburg and Prussia
Northern March
965–983 Old Prussians
pre-13th century
Lutician federation
983 – 12th century
Margraviate of Brandenburg
1157–1618 (1806) (HRE)
(Bohemia 1373–1415) Teutonic Order
1224–1525
(Polish fief 1466–1525)
Duchy of Prussia
1525–1618 (1701)
(Polish fief 1525–1657) Royal (Polish) Prussia (Poland)
1454/1466 – 1772
Brandenburg-Prussia
1618–1701
Kingdom in Prussia
1701–1772
Kingdom of Prussia
1772–1918
Free State of Prussia (Germany)
1918–1947 Klaipėda Region
(Lithuania)
1920–1939 / 1945–present Recovered Territories
(Poland)
1918/1945–present
Brandenburg
(Germany)
1947–1952 / 1990–present Kaliningrad Oblast
(Russia)
1945–present
The main coat of arms of Prussia, as well as the flag of Prussia, depicted a black eagle on a white background.
The black and white national colours were already used by the Teutonic Knights and by the Hohenzollern dynasty. The Teutonic Order wore a white coat embroidered with a black cross with gold insert and black imperial eagle. The combination of the black and white colours with the white and red Hanseatic colours of the free cities Bremen, Hamburg and Lübeck, as well as of Brandenburg, resulted in the black-white-red commercial flag of the North German Confederation, which became the flag of the German Empire in 1871.[ citation needed ]
Suum cuique (“to each, his own”), the motto of the Order of the Black Eagle created by King Frederick I in 1701, was often associated with the whole of Prussia. The Iron Cross, a military decoration created by King Frederick William III in 1813, was also commonly associated with the country.[ citation needed ] The region, originally populated by Baltic Old Prussians who were Christianised, became a favoured location for immigration by (later mainly Protestant) Germans ( see Ostsiedlung ), as well as Poles and Lithuanians along the border regions.
Territory[edit]
Before its abolition, the territory of the Kingdom of Prussia included the provinces of West Prussia; East Prussia; Brandenburg; Saxony (including much of the present-day state of Saxony-Anhalt and parts of the state of Thuringia in Germany); Pomerania; Rhineland; Westphalia; Silesia (without Austrian Silesia); Schleswig-Holstein; Hanover; Hesse-Nassau; and a small detached area in the south called Hohenzollern, the ancestral home of the Prussian ruling family. The land that the Teutonic Knights occupied was flat and covered with fertile soil. The area was perfectly suited to the large-scale raising of wheat.[6] The rise of early Prussia was based on the raising and selling of wheat. Teutonic Prussia became known as the “bread basket of Western Europe” (in German, Kornkammer , or granary). The port cities of Stettin (Szczecin) in Pomerania, Danzig (Gdańsk) in Prussia, Riga in Livonia, Königsberg (Kaliningrad), and Memel (Klaipėda) rose on the back of this wheat production. Wheat production and trade brought Prussia into a close relationship with the Hanseatic League during the period of time from 1356 (official founding of the Hanseatic League) until the decline of the League in about 1500.
The expansion of Prussia based on its connection with the Hanseatic League cut both Poland and Lithuania off from the coast of the Baltic Sea and trade abroad.[7] This meant that Poland and Lithuania would be traditional enemies of Prussia, which was still called the Teutonic Knights.[8]
History[edit]
Further information: Kingdom of Prussia
Teutonic Order[edit]
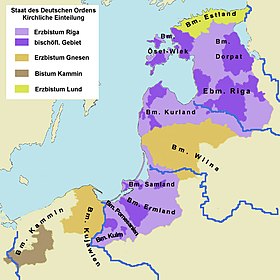
Situation after the conquest in the late 13th century. Areas in purple under control of the Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights

The Teutonic Order (orange) following the Second Peace of Thorn (1466)
Main article: Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights
In 1211 King Andrew II of Hungary granted Burzenland in Transylvania as a fiefdom to the Teutonic Knights, a German military order of crusading knights, headquartered in the Kingdom of Jerusalem at Acre. In 1225 he expelled them, and they transferred their operations to the Baltic Sea area. Konrad I, the Polish duke of Masovia, had unsuccessfully attempted to conquer pagan Prussia in crusades in 1219 and 1222.[9] In 1226 Duke Konrad invited the Teutonic Knights to conquer the Baltic Prussian tribes on his borders.
During 60 years of struggles against the Old Prussians, the Order established an independent state that came to control Prūsa. After the Livonian Brothers of the Sword joined the Teutonic Order in 1237, the Order also controlled Livonia (now Latvia and Estonia). Around 1252 they finished the conquest of the northernmost Prussian tribe of the Skalvians as well as of the western Baltic Curonians, and erected Memel Castle, which developed into the major port city of Memel (Klaipėda). The Treaty of Melno defined the final border between Prussia and the adjoining Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1422.
The Hanseatic League officially formed in northern Europe in 1356 as a group of trading cities. This League came to hold a monopoly on all trade leaving the interior of Europe and Scandinavia and on all sailing trade in the Baltic Sea for foreign countries.[10] The merchants of the interiors of Sweden, Denmark, and Poland came to feel oppressed by the Hanseatic League.[ citation needed ]
In the course of the Ostsiedlung (German eastward expansion) process, settlers were invited[ by whom? ], bringing changes in the ethnic composition as well as in language, culture, and law of the eastern borders of the German lands. As a majority of these settlers were Germans, Low German became the dominant language.
The Knights of the Teutonic Order were subordinate to the papacy and to the emperor. Their initially close relationship with the Polish Crown deteriorated after they conquered Polish-controlled Pomerelia and Danzig (Gdańsk) in 1308. Eventually, Poland and Lithuania, allied through the Union of Krewo (1385), defeated the Knights in the Battle of Grunwald (Tannenberg) in 1410.
The Thirteen Years’ War (1454–1466) began when the Prussian Confederation, a coalition of Hanseatic cities of western Prussia, rebelled against the Order and requested help from the Polish king, Casimir IV Jagiellon. The Teutonic Knights were forced to acknowledge the sovereignty of, and to pay tribute to Casimir IV in the Second Peace of Thorn (1466), losing western Prussia (Royal Prussia) to Poland in the process. Pursuant to the Second Peace of Thorn, two Prussian states were established.[11][ need quotation to verify ]
During the period of the monastic state of the Teutonic Knights, mercenaries from the Holy Roman Empire were granted lands by the Order and gradually formed a new landed Prussian nobility, from which the Junkers would evolve to take a major role in the militarization of Prussia and, later, Germany.[12]
Duchy of Prussia[edit]

Prussian Homage by Jan Matejko. After admitting the dependence of Prussia to the Polish Crown, Albert of Prussia receives Ducal Prussia as a fief from King Sigismund I the Old of Poland in 1525
Main articles: Prussian Homage, Duchy of Prussia, and Crown of the Kingdom of Poland
On 10 April 1525, after signing of the Treaty of Kraków, which officially ended the Polish–Teutonic War (1519–21), in the main square of the Polish capital Kraków, Albert I resigned his position as Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights and received the title “Duke of Prussia” from King Zygmunt I the Old of Poland. As a symbol of vassalage, Albert received a standard with the Prussian coat of arms from the Polish king. The black Prussian eagle on the flag was augmented with a letter “S” (for Sigismundus) and had a crown placed around its neck as a symbol of submission to Poland. Albert I, a member of a cadet branch of the House of Hohenzollern became a Lutheran Protestant and secularized the Order’s Prussian territories.[13] This was the area east of the mouth of the Vistula River, later sometimes called “Prussia proper”. For the first time, these lands came into the hands of a branch of the Hohenzollern family, who already ruled the Margraviate of Brandenburg, since the 15th century. Furthermore, with his renunciation of the Order, Albert could now marry and produce legitimate heirs.
![]()








